
Produce personalized presentation boards that distill complex concepts into simple visual representations with a few helpful tools and effects.


Produce personalized presentation boards that distill complex concepts into simple visual representations with a few helpful tools and effects.

For the past two years, we have found ourselves wanting to highlight what is the foundation of architectural practice: the architectural drawing. We realized that even after almost a decade of publishing the best projects from around the world, we should take on the task of singling out the exceptional cases of representation, taking into account all varieties and species of drawings. Following up on the criteria used in the previous edition, all the architectural drawings we have selected this year have a sensitive expression— whether it be artistic, technical or conceptual—and they all aim to express and explain the respective project using simplicity, detail, textures, 3D and color as main tools.
Below you will see the selection of drawings arranged under eight categories: Architectural Drawings, Axonometrics, Context, Diagrams, Sketches, Animated Gifs, Details and Other Techniques.

Letters of recommendations are strange in that we all know what they are, but save for the people who are actually using them to evaluate a candidate, what happens with the letter is shrouded in mystery. Can a stellar recommendation letter make up for a less-than-stellar transcript? Are you going to be removed from consideration because your recommender didn't make you sound like Captain Awesome? It all depends—but as long as these letters are required for admissions processes and grants and other things, we'll shed some light on how to ask for (and/or write) a letter of recommendation.
Whether you're on the asking end or the writing end, there are some basic tips and rules that should be followed. (Why should you trust me? Because I've asked for letters and written letters and things have worked out pretty well for all involved parties.)

A discipline like accounting might seem very different from the world of architecture. In architecture, creativity is revered, but in accounting, it usually entails fraud. Still, you can’t work if your firm is failing, and accounting is vital to success. Beyond the upkeep of your business, though, there are other ways that accounting can affect your work in a meaningful way.

“Will you look at that? St. Mark’s Square is flooded!” An Australian day tripper is astonished. “This place is actually sinking,” her friend casually exclaims. They, like so many I’ve overheard on the vaporetti, are convinced that the Venetian islands exist on a precipice between the fragility of their current condition and nothing short of imminent submersion. With catastrophe always around the corner a short break in Venice is more of an extreme adventure trip than a European city-break. If it were true, that is.

The inclusion of cars in photographs of architecture is an interesting tool that can help the viewer to understand the scale of a building. The addition of an automobile to a scene can not only help to transmit a notion of the size of the photographed elements, it can also be used to generate interesting compositional relationships to benefit the photograph as a whole. Below, we've highlighted a selection of 10 images from prominent photographers such as Rafael Gamo, Michael Sinclair and Bruno Candiotto which make effective use of this technique.

In this collaboration, the Spanish office Ecosistema Urbano analyzes the rise and fall of the shopping centers as an authentically American typology of the twentieth century and with commercial success in the rest of the world, although it does not undergo significant changes in "its spaces, solutions, and elements."
According to the authors, this typology is currently undergoing an inflection due to the new economic and urban paradigms that force them to reinvent themselves or die. They plan a series of revitalization strategies in a mall in the outskirts of Barcelona (Spain) that seeks their "reconfiguration through the introduction of new programs in an attempt to convert it into a much more public space, being able to attract users who would otherwise not come."
Full article after the break.

Douglas Barnhard, the owner of the home decor company Sourgrassbuilt, designs and builds birdhouses. Built out of repurposed materials, his designs are inspired by mid-century modernism and pay homage to the likes of Frank Lloyd Wright, Joseph Eichler and the Bauhaus School in Germany yet mix with Barnhard's experience of the rich surf and skate scene in Santa Cruz.

This article was originally published by Common Edge as "Africa’s Undeclared War on the Disabled."
Recently I spent part of a week in the company of a multidisciplinary group of academics and researchers from Europe, the US, and Africa, at a workshop entitled “The Practice and Politics of DIY Urbanism in Africa.” Jonathan Makuwira, a professor from the Malawi University of Technology, delivered a compelling paper on “Disability and Urbanism in Malawi,” highlighting the many challenges of the continent’s disabled population, using that city as a case study.
The lecture reaffirmed my sentiments on the gross inadequacies of urban public spaces for the disabled. It’s an issue that formed the basis for my 2016 entry for the Richard Rogers Fellowship at the Harvard Graduate School of Design (GSD), where I had proposed to use the fellowship to develop a prescriptive accessible design blueprint for public spaces in the city of Abuja.

Sustainability. A word that, for many of us, has been driven into our minds from the very start of our careers as architects. We have a responsibility to the planet and future generations to design buildings that are socially conscious—from solar panels to triple-glazed windows, we have tried it all.
Ultimately, whether our designs are sustainable comes down to the early decisions we make for the building, with our choice of materials having a huge effect on the overall carbon footprint. With new technologies come new ways of incorporating abundantly found materials into the skin of the building that could reduce the building's embodied energy and enhance the structure's properties.
In this article, we have compiled a list of 8 familiar materials that you wouldn't initially associate with sustainability but which you might consider for your next design.

As a construction material, bamboo is resistant, versatile, grows rapidly and is immensely friendly with its own ecosystem and its agroforestry environment. In addition, it presents a large number of species that deliver different diameters and heights. But are there also variations in its color?
We are truly impressed with the work of architects, builders, and artisans who use 'blond bamboo,' which moves between yellow and brown tones. These species are abundant and easy to harvest, and therefore are more common and accessible. However, there are a number of species that have a darker coloration and could revolutionize bamboo architecture in the future. Here we present black bamboo.

December 21 saw the winter solstice in the northern hemisphere. The season is an excellent time to take architectural photographs in a unique and different landscape, with a blanket of snow providing a reminder of the delights of nature. Here, we present a selection of 10 cabins captured in winter by prominent photographers such as Tim Bies, Fernando Alda and Pasi Aalto.

"Bamboo is close to an ideal structural material." This statement by Neil Thomas during his talk at Bamboo U, which took place in November 2017 in Bali, really caught my attention. Neil is the founding director of atelier one, a London office of structural engineering, whose outstanding projects include stage and scenography for the Rolling Stones, Pink Floyd, and U2; art installations by Anish Kapoor and Marc Quinn; the Gardens by the Bay, in Singapore, among many others. From the last few years, the engineer has exhaustively studied about bamboo, its structural properties and its most diverse potential.

More than half of the planet is composed of water and most of the population lives in its vicinity. These sites are increasingly affected by environmental disasters or the increase in water levels caused by global warming, forming a scenario that brings new challenges to the way we live and think the buildings in coastal or riverine areas.
Floating architecture can adapt to changes in water levels and different climatic conditions, signaling a possible way to solve the problems pointed out. To increase your repertoire of floating references, we have gathered here 15 projects that have been implemented directly in the waters and have the most different uses: housing, cultural, educational, recreational and infrastructure.
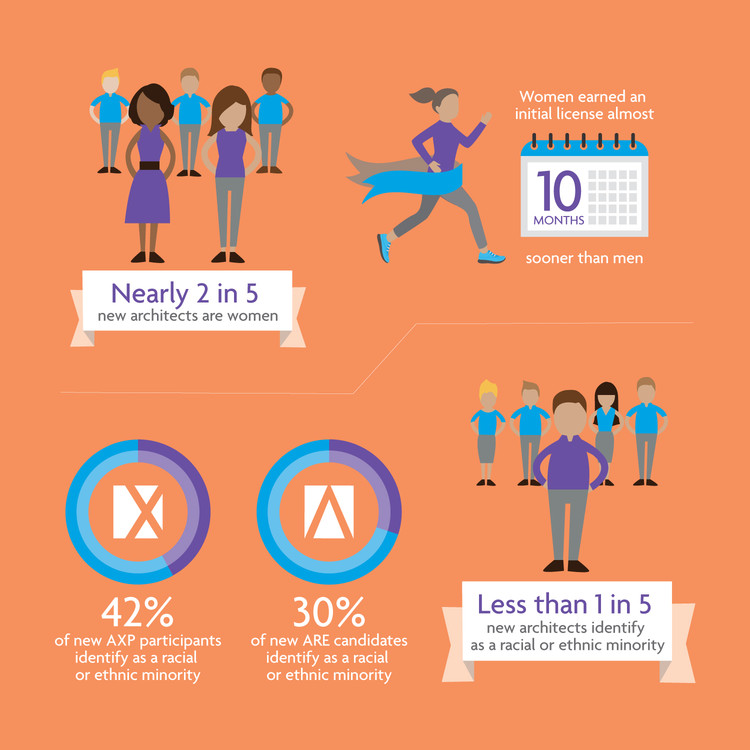
It’s no secret that the architecture field struggles with diversity. Both personal stories and deeper studies detail the profession’s lack of representation. But despite concerns suggesting diversity in the field remains stagnant, there’s good news: the latest data from the National Council of Architectural Registration Boards (NCARB) reveals that gender, racial, and ethnic diversity is slowly improving.
The 2017 edition of NCARB by the Numbers (NCARB’s annual data report) indicates that while the number of architects and licensure candidates holds steady, the pool of individuals is more diverse than ever before. Although there is still much room for improvement, this data provides an encouraging glimpse into the future of the profession.
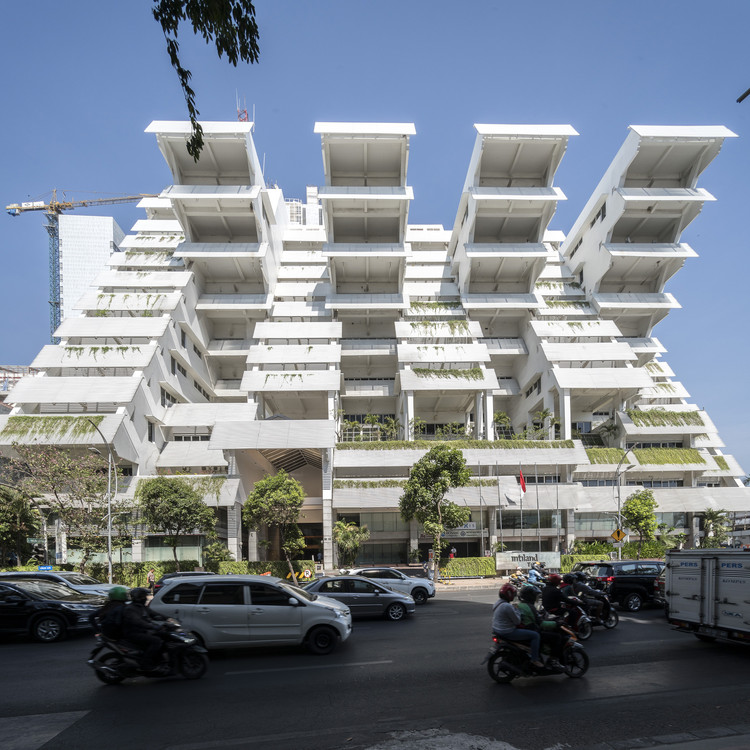

To speak of Paul Rudolph’s illustrious career is to trace a grand arc stretching from the 1940s to the 1990s. More often than not, the popular narrative begins with his student days at Harvard under the tutelage of Walter Gropius, touches upon his earliest, much-loved Florida beach houses, circles around his eventual break from the rigidity of both the Sarasota School and the International Style, and finally races towards the apex: his chairmanship of the Yale School of Architecture, and the concurrent shift to a Brutalist architectural style characterized by monumental forms, rugged concrete, and interwoven, multilevelled spaces awash with a remarkable interplay of light. Then comes the fall from grace: the beloved Yale Art and Architecture Building went up in flames just as the architecture profession began to question modernist ideals, and eventually Postmodernism was ushered in. Flickering, sputtering, Rudolph's grand narrative arc lurched towards Southeast Asia, bearing away the “martyred saint.” Save for several scattered commissions in the United States, Rudolph spent the last two decades of his life building abroad, mostly across Hong Kong, Indonesia, and Singapore, until his death in 1997.
But of course, time and again, historians have sought to challenge the myth of the failed architect by rereading his understudied work from the late years. Adding to this growing corpus of fresh research and alternate perspectives is architectural photographer Darren Soh’s ongoing project documenting—so far—three of Rudolph’s major works in Southeast Asia: The Colonnade (1986) and The Concourse (1994) in Singapore, and the Intiland Tower (1997) in Surabaya, Indonesia.

This article was originally published on the blog of the Chicago Architecture Biennial, the largest platform for contemporary architecture in North America. The 2017 Biennial, entitled Make New History, will be free and open to the public between September 16, 2017 and January 6, 2018.
When we think of contemporary architecture in China, we often refer to the megaprojects by international architecture studios that tend to get covered most in the design media. From OMA’s CCTV Headquarters and Shenzhen Stock Exchange to the recently completed Tianjin Binhai Library by MVRDV and Poly International Plaza by SOM, these projects dominate urban skylines at a singular scale that suggests they were built to impress.
Beyond individual buildings, China’s mega-architecture boom is rapidly developing entirely new cities, a process designed to relieve the country’s principal metropolitan areas of their high density, while offering new prototypes for urban life. These highly branded environments are prompting displacement – as a form of rural exodus – and social stress throughout the country, while also ignoring the legacy of traditional Chinese architecture in urban centers.
.jpg?1513724004)

The architectural model: a tool, a sculptural artifact, a prized possession, and yet in the digital age of BIM and Virtual Reality, perhaps becoming an enigma, a relic for settling dust. And yet, we are still making them. If you imagine that famous photo of earth from space, of every model ever made in a single image, it raises the question - where are they all? Where does the architectural model go to die?

Architects are people of great taste, who enjoy the finer things in life – especially when it comes to pens. The saying goes: ‘don’t judge a book by its cover’, but inevitably we find ourselves judging an architect by their choice of pen. It’s easy to do when your colleague decides to grab the nearest biro to sketch a quick diagram, leaving you to squirm as you sit and watch it indent the paper.
Pens are powerful tools for architects, that harness our thoughts and ideas into potential three-dimensional structures. In the age of the digital world, pens have become sacred, grounding us back to the simple pleasure of drawing to begin the creative process. After years of trying and testing all the different writing instruments out there, we eventually find the one which can say a lot more about ourselves than you may think.

Theatre Projects consultants, together with the architectural office Studio KO, have designed a multipurpose auditorium of 115 seats, with the aim of hosting conferences, screenings, concerts, theater, and cinema.
The auditorium is part of the new Museum Yves Saint Laurent Marrakech, and incorporates a series of elements and technologies that allow for high-quality sound and lighting, as well as ensuring total flexibility of the room to adapt to all required uses.

The Fundación EcoInclusión - winner of the first prize in the regional competition Google.org Challenge - is an Argentine non-profit organization that was born in 2015, from the hands of a group of young people that promote the construction of a fairer, equitable and sustainable society.
Located in the Alta Gracia city, province of Córdoba, Ecoinclusión works in the reduction of PET bottles waste with the production of bricks made of plastic residues destined to the construction in vulnerable sectors, with the aim of generating environmental and social impact and cultural participation in the communities.

Do you think architecture is your calling? Do you have the passion and drive to explore this creative field and learn from the best? Every year, many young people decide to take on the challenge of an architecture education, but how many have any idea what is in store for them on that first day in the design studio? In truth, the exercises given to new students by their professors reveal a lot about the architecture world.
I reached out to hundreds of professors, assistant professors, and adjunct and visiting professors to find out their favorite first-year studio design prompt. The responses varied from the abstract to the concrete, as well as from simple drawing exercises to complex steps to end at a completed work. Most projects were designed for individuals, however some required a team effort. The following is a peek into that world from a variety of educators from schools around the globe.

Unbeknown to many, cork is something of a dark horse when it comes to the environment—a model of a sustainable industry and building material. By its very nature, cork is both recyclable and renewable, as it is the only tree that regenerates its bark, while harvesting that bark causes the tree no harm.
Cork has been sneaking its way into our buildings for many years now; due to its hard-wearing properties it can be found, for example, in the checkerboard flooring of the Library of Congress. Even NASA has been wise to cork's light weight and insulation capacity, using it as an insulator for their space shuttles.

This article was originally published by Autodesk's Redshift publication as "Next-Gen Virtual Reality Will Let You Create From Scratch—Right Inside VR."
The architecture and manufacturing industries are about to undergo a radical shift in how they make things. In the near future, designers and engineers will be able to create products, buildings, and cities in real time, in virtual reality (VR).
In predicting VR’s dramatic evolution, an analogy to early cinematic history is apt: As one legend has it, when the motion-picture camera first came out, actors were filmed on a set, in front of fake trees. Then someone said, “Why don’t you just put the camera in the forest?” Simple, but game-changing. VR technology is already available, and it’s only a matter of time before it is used to its full potential.

Established by Hyundai Group, Hyundai Motorstudio Beijing was opened in the 798 Art Zone in Beijing on November 1, 2017. The large-scale panoramic mural 798 commissioned by Hyundai and created by Drawing Architecture Studio was officially released at the same time.
Around 14.5 meters in width and 12.7 meters in height, the mural takes the 798 Art Zone as the representative to depict the status of today’s city in the context of information overload. The drawing is a narrative map: most architectural renderings in the panorama are based on actual prototypes at 798. The assemblages are shattered, fragmented and free-floating. Enormous power comes from the inherent vitality and energy of the city. Its shell is cracked and broken to reveal the exciting maze of life inside. 798 is an imaginary representation of the real world, a reconstruction of countless fragments of physical space and time, that constantly collide, align and rearrange.