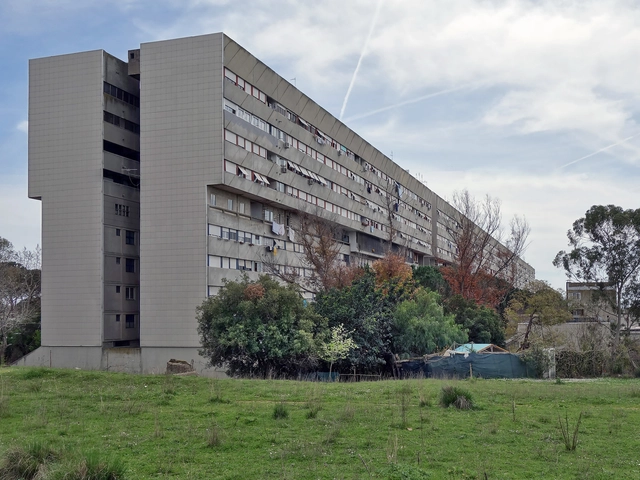
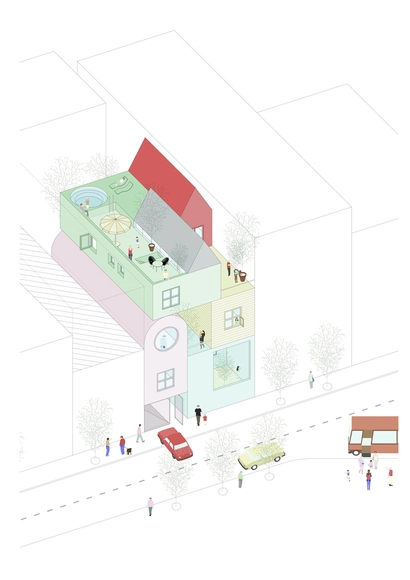
The Corviale housing complex, located in the south-western periphery of Rome, was designed in the 1970s as a solution to the growing number of dormitory districts in the Roman suburbs, caused by the significant population increase between the 1950s and 1970s - when the population grew from approximately 1.6 million to 2.7 million inhabitants - followed by suburban sprawl.
The project, also known as Serpentone because of its huge proportions, was developed by a team of architects under the leadership of Mario Fiorentino between 1972 and 1974. Construction took place between 1973 and 1982, but the original plan to use the fourth floor of the main building for commercial uses, services, and common areas, was dropped because the contractor went bankrupt. The floor was eventually taken over by informal settlements, and this event is considered to be the root of the problems with this emblematic project in the history of housing in Italy.

























.jpg?1446087581&format=webp&width=640&height=580)
.jpg?1446087961)
.jpg?1446087940)
.jpg?1446087843)
.jpg?1446087801)
.jpg?1446087581)
.jpg?1434000059&format=webp&width=640&height=580)
.jpg?1433999851)
.jpg?1434000047)
.jpg?1433999828)
.jpg?1434000001)
.jpg?1434000059)




















































