Produce personalized presentation boards that distill complex concepts into simple visual representations with a few helpful tools and effects.
Articles
How to Create Architectural Presentation Boards
The Gherkin: How London’s Famous Tower Leveraged Risk and Became an Icon (Part 2)

This four part series (originally published on Aggregate’s website) examines The Gherkin, the London office tower designed by Foster + Partners, showing how the urban icon engaged and leveraged perceptions of risk. In part one, author Jonathan Massey introduced the concept of "risk design” to describe how the Gherkin’s design managed the risks posed by climate change, terrorism, and globalization. In part two, below, Massey examines the Gherkin’s enclosure and ventilation systems in detail to explain how the building negotiated climate risk.
In a poster promoting London’s bid to host the Olympic Games, the Gherkin supported gymnast Ben Brown as he vaulted over the building’s conical peak. The image associated British athleticism and architecture as complementary manifestations of daring and skill, enlisting the Gherkin as evidence that London possessed the expertise and panache to handle the risk involved in hosting an Olympic Games.
But a poster created three years later offered a very different image. Created by activists from the Camp for Climate Action to publicize a mass protest at Heathrow Airport against the environmental degradation caused by air travel, this poster shows the Gherkin affording only precarious footing to a giant polar bear that swats at passing jets as its claws grasp at the slight relief offered by spiraling mullions and fins.
Unified Architectural Theory: Chapter 3
.jpg?1384172762&format=webp&width=640&height=580)
We will be publishing Nikos Salingaros’ book, Unified Architectural Theory, in a series of installments, making it digitally, freely available for students and architects around the world. The following chapter posits that architecture's geometric structure determines its "vitality," a quality that should be the basis of architectural critique; it also explains If you missed them, make sure to read the introduction, Chapter One, Chapter 2A, and Chapter 2B first.
The perceived quality of life in buildings and urban spaces comes from the geometry (the form of structures on all scales, and their coherence), and how that geometry connects to the individual. It also catalyzes interactions among people — if it is done successfully.
The easiest way to perceive this quality of “life” is to compare pairs of objects or settings and judge intuitively which one has more “life”. After a series of such experiments, it becomes obvious that degree of “life” in architecture arises from geometrical structure.
Does the Title of "Architect" Deserve To Be Protected?

In August, the AIA posted a topic on its LinkedIn discussion board entitled "Misrepresenting Oneself as an Architect on LinkedIn". Ever since (and once again), the issue of protecting the title of "Architect" has been a hot topic, as explained in this article on Fast Company. This follows the revelation in BD last year that the Architects' Registration Board ordered the British architectural media to cease referring to Renzo Piano and Daniel Libeskind as Architects. With the topic appearing so frequently, and in different countries each time, Fast Company conjures images of a "raging global debate". But what, really, is going on in the world of architecture to fuel such a debate? Read on to find out more.
The Gherkin: How London's Famous Tower Leveraged Risk and Became an Icon

How does design change the nature and distribution of risk? In this, the first of four installments examining the Gherkin, the London office tower and urban icon designed by Foster + Partners, author Jonathan Massey introduces the concept of “risk design.” The series, originally published on Aggregate's website, explains how the Gherkin leveraged perceptions of risk to generate profits, promote economic growth, and raise the currency of design expertise.
Designing Risk
Back the Bid. Leap for London. Make Britain Proud. Emblazoned across photomontages of oversized athletes jumping over, diving off, and shooting for architectural landmarks old and new, these slogans appeared in 2004 on posters encouraging Londoners to support the city’s bid to host the 2012 Olympic Games. Featured twice in the series of six posters—along with Buckingham Palace, Nelson’s Column, the Tower Bridge, the London Eye, and the Thames Barrier—was 30 St Mary Axe, the office tower known colloquially as the Gherkin for its resemblance to a pickle, or as the Swiss Re building, after the Zurich-based reinsurance company that commissioned the building and remains its major tenant.
London Calling: The Man Behind the Stirling Prize

A few weeks ago the RIBA doled out the 18th Stirling Prize to London-based architects Witherford Watson Mann. The decision was a good one. It was good for WWM and good for the profession – a youngish practice being recognized for a small but beautiful piece of work.
The scheme’s application of brickwork and joinery removes the work from the expediencies of modern construction technology and building products, which almost exclusively characterize the contemporary built environment. It genuinely feels like a project made at a different point in history, the result of the quite particular interests of three minds, Stephen Witherford, Chris Watson and William Mann. It is direct and personal. It reminds me of Stirling’s work..
And not just for its powerful draftsmanship, plan and restricted palette of materials, but for its intimacy. An intimacy that is apparent in much of Stirling’s oeuvre. I do not refer to the production of intimate spaces per se but the formulation of an architecture that is authored not by a factory but a few minds.
The latest Stirling prompted me to look back, and reconsider the work of Stirling himself.
Museu Brasileiro de Escultura (MuBE) / Paulo Mendes da Rocha

Keep an eye out, or you might miss the Museu Brasileiro de Escultura (a.k.a. MuBE, pronounced MOO-bee). Widely considered the masterpiece of Pritzker Prize-winner Paulo Mendes da Rocha, the building was in fact born out of the desire to have no building at all. When in the 1980s an empty lot in Sao Paulo's mansion-laden Jardins district was slated to become a shopping mall, wealthy residents successfully lobbied to create a public square instead. To sweeten the deal and ensure the land stayed commercial-free, they hired Mendes de Rocha to create MuBE. Completed in 1995, the 7000-sq-meter museum hunkers down beneath ground level, thus preserving what in Sao Paulo is that rarest of luxuries: a public green space.
Cities are for People: Turning Underused Spaces into Public Places

It begins with a fundamental premise: Buildings occupy only a fraction of land in cities. Just as important as physical structures, are the public spaces in between.
In many cities these spaces have long been disregarded. Today, however, we are witnessing bold experimentation and innovation coming forth from cities across the globe: cities re-using and re-imagining previously underused spaces in order to uplift communities and transform lives.
Light Matters: Europe's Leading Light Festivals

In mid autumn, when the nights get longer in the northern hemisphere, we encounter numerous light festivals. And indeed, within the last ten years, more and more light festivals have globally emerged. The reason for the success of light festivals is simple, as the German curator Bettina Pelz concludes: “It’s actually fairly easy, because whenever you do something with light in cities in the night, then people do come. If you do it good, they come twice.”
As Pelz points out, light is an apt medium for evening events, since it easily attracts people. Communities have discovered the potential of lighting for city marketing, and the closer they plan their date to Christmas, the more they merge their illumination with the festive blinking lights of commercial Christmas markets.
Join us on a tour through some of the leading light festivals in Europe. Read more about their different backgrounds, artistic concepts and future trends after the break...
The Indicator: A Rebuttal to "Why I Left the Architecture Profession"

Christine Outram’s rant “Why I Left the Architecture Profession” is an honest and seemingly spontaneous attempt at staking out a position against an “outdated” profession. It’s explosive in its assertion that “you,” meaning all you architects, are out of touch. “You” don’t listen to your clients. “You” are obsessed with form-making. “You” are a soulless machine, designing by code templates and cut and paste, with no regard for humanity. Her essay hits like a splatter bomb, throwing shrapnel in all directions. It’s a drone strike that has killed innocents. It’s clumsy and reckless.
It begs to be deconstructed. It demands a counterattack. And, judging from the lengthy comment thread, this is what it has reaped. Be that as it may, the issues are obvious. Telling architects they are “outdated” or that they don’t listen seems like a calculated attempt to get the attention of architects and to get them to somehow prove themselves, to make them mad in ways equal to her own anger.
Well, it’s got my attention. Here’s my rebuttal.
Why Hollywood Needs to Change its Conception of "The Architect"
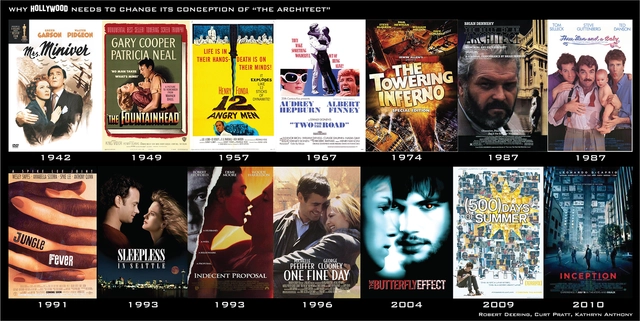
Writers, directors, producers, and actors in the Hollywood film industry play major roles in shaping how millions around the world perceive architects and the architectural profession. Television shows, too, create stereotypes of professions that are repeatedly drummed into the brain with each successive episode. Both make long-lasting impacts that may encourage or dissuade young people from pursuing architecture as a career.
Is The Demolition of Prentice Hospital Another "Penn Station Moment"?

This article, by Michael R. Allen, was originally published on Next City as "Prentice Hospital Could Become Modernism's 'Penn Station Moment'"
When the concrete cloverleaf of Prentice Hospital sprouted from the Chicago ground in 1975, its award-winning design met the praise of critics and the admiration of many Chicagoans. Architect Bertrand Goldberg drew from Brutalism, but with a symmetry and grace that distinguished Prentice from more angular works in that style.
This week, as Goldberg’s famous work is pulled apart by wreckers, nothing about its loss seems symmetrical or graceful. Within 40 years, the building transitioned from a proud symbol of civic renewal and design innovation to the victim of old-fashioned Chicago politics. The controversy surrounding the demolition of Prentice, however, injected the preservation movement into an urban design discussion with a presence not seen in a long time.
Three Arup Specialists Share Their Vision of The Future of Healthcare Design

This interview was originally posted on Arup Connect and titled "Global perspectives on the future of healthcare design".
In the last few decades, rapid advances in both medical and consumer technologies have created revolutionary possibilities for every aspect of healthcare, from prevention to diagnosis to treatment and beyond. From DNA-based preventative care to digital appointments with doctors thousands of miles away, the future holds enormous potential for improving longevity and quality of life for people around the world.
These dynamics present significant challenges for designers working to shape a built environment that will meet healthcare needs both today and in the future. We spoke with Arup experts from around the globe — Phil Nedin, who heads the firm’s global healthcare business from London; Bill Scrantom, the Los Angeles-based healthcare leader for North and South America; and Katie Wood, who recently relocated from Australia to Toronto to build the Canadian practice — to learn more.
Why I Left the Architecture Profession

In the following article, which originally appeared on Medium as "What Starbucks Gets that Architects Don't," Christine Outram, bemoans that architects today just don't listen to people's actual needs.
Dear architects,
You’re outdated. I know this because I once was one of you. But now I’ve moved on. I moved on because despite your love of a great curve, and your experimentation with form, you don’t understand people.
I correct myself. You don’t listen to people.
Unified Architectural Theory: Chapter 2B

We will be publishing Nikos Salingaros’ book, Unified Architectural Theory, in a series of installments, making it digitally, freely available for students and architects around the world. Part one of Chapter Two outlined the scientific approach to architectural theory; the following, part two of Chapter Two, explains why Salingaros considers this approach to be superior to that taken by deconstructivists. If you missed them, make sure to catch up on the introduction, Chapter 1, and Chapter 2A.
Some traditions are anachronistic and misguided, but as reservoirs of traditional solutions against which to check new proposals they are of immense importance. A new solution may at some point replace a traditional solution, but it must succeed in reestablishing the connections to the rest of knowledge. In the context of social patterns, architecture, and urbanism, new solutions are useful if they connect to traditional social, architectural, and urban patterns (i.e., all those before the 1920s). If there is an obvious gap where nothing in a discipline refers to anything outside, then there could be a serious problem.
Recently, Edward Wilson has introduced the notion of “consilience” as “the interlocking of causal explanations across disciplines” (Wilson, 1998a). Consilience claims that all explanations in nature are connected; there are no totally isolated phenomena. Wilson focuses on incomplete pieces of knowledge: the wide region separating the sciences from the humanities. He is happy to see it being slowly filled in by evolutionary biologists, cognitive neuroscientists, and researchers in artificial intelligence. At the same time, he is alarmed by people in the humanities who are erasing parts of the existing body of knowledge. These include deconstructive philosophers. Wilson characterizes their efforts as based on ignorance.
The Indicator: Ten Years Later, Has the Disney Concert Hall Made a Difference?

On October 23rd, the Walt Disney concert hall, the project that almost never was, will celebrate its ten-year anniversary. Throughout these ten years it has had all manner of transformative power attributed to it. But has it really transformed LA? What would the city have been like if it had never been built? Would it be fundamentally different?
The answer? No.The city wouldn’t even be that different in the immediate vicinity of Grand Avenue.
Talking With Thom

Despite what you may think, Thom Mayne isn't the "bad boy" of architecture - at least, not according to Thom Mayne. He sees himself more as a skilled negotiator than a starchitect (a phrase he hates) - after all, he reasons, how else would he have completed so many buildings? In this interview, originally published on Metropolis Magazine's Point of View blog as "Q&A: Thom Mayne," Andrew Caruso and Mayne discuss Morphosis, SCI-ARC, the early days of his career, and his architectural ethos.
Andrew Caruso: Your professional career began in the discipline of planning. What led to the shift toward architecture and your eventual partnership with Jim Stafford?
Thom Mayne: I started working at the Pasadena redevelopment agency doing low cost housing, and that’s where I met Jim [Stafford]. Coming out of USC, I had no background about Mies, Khan or Corbusier, for example. USC was very strong in being anti-historical, looking forward instead of backward. I was essentially naive.
Jim was a year ahead of me at USC and had part of the older regime at the school. When I met him at the planning agency, he started introducing me to history. I got fascinated by [Paul] Rudolph; and then it just took off. Jim guided me through this thought process, reestablishing me in the tradition of architecture.
Robots, Cars and Architecture
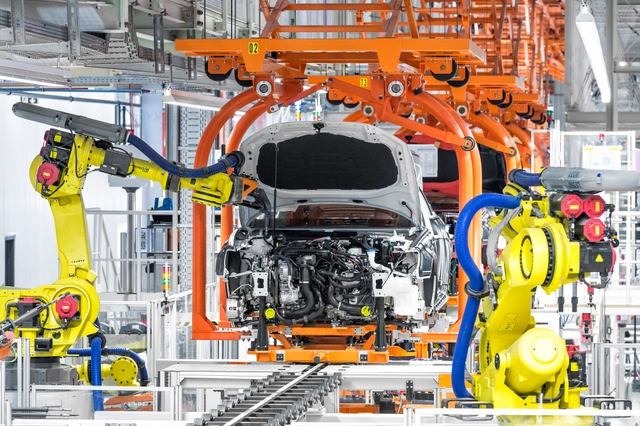

Since the dawn of the modern era, there has been a strong relationship between architecture and the car, especially in the works of Le Corbusier.
Le Corbusier was fascinated by his car (the Voisin C7 Lumineuse); the aesthetics of this functional, mass produced machine deeply influenced his designs. Its focus on function translated into his concept that houses should be "machines for living" and inspired a series of experiments of mass produced, pre-fab houses (such as the Maison Citrohan). Most of these concepts were later materialized in the iconic Villa Savoye, whose floorplan was even designed to accommodate the car's turning radius.
Beyond the Tent: Why Refugee Camps Need Architects (Now More than Ever)

In 2013 alone some 1 million people have poured out of Syria to escape a civil conflict that has been raging for over two years. The total number of Syrian refugees is well over 2 million, an unprecedented number and a disturbing reality that has put the host countries under immense infrastructural strain.
Host countries at least have a protocol they can follow, however. UN Handbooks are consulted and used to inform an appropriate approach to camp planning issues. Land is negotiated for and a grid layout is set. The method, while general, is meticulous – adequate for an issue with an expiration date.
Or at least it would be if the issue were, in fact, temporary.
Public School 158 Bayard Taylor Library / Atelier Pagnamenta Torriani

Architects: Atelier Pagnamenta Torriani Location: 1458 York Avenue, New York, NY 10075, USA Area: 0.0 m2 Year: 2011 Photography: Courtesy of Atelier Pagnamenta Torriani
Awards Competition Boosts Momentum of Sustainable Construction
.jpg?1381430654&format=webp&width=640&height=580)
Since 2005 more than 150 projects advancing sustainability of the built environment haven been celebrated in the Holcim Awards as outstanding, innovative and inspiring examples of sustainable construction. Winning a prize in this international competition has sign-posted professional success for the project teams; highlighted sustainability on the public agenda; accelerated tangible change for urban poor; and secured funding for environmental recovery and research. Beyond holding a trophy aloft, the momentum of sustainable construction has continued for the architects behind projects in locations as diverse as Burkina Faso, Spain, India, and Canada.
More after the break.
Could a Silicon Valley Entrepreneur Revolutionize Healthcare Design?

This article, originally posted in Metropolis Magazine as "Derek Parker's Third Act," tells the story of Aditazz, a Silicon Valley design startup founded by Deepak Aatresh, an entrepreneur with a background in silicon chip manufacturing. Now in collaboration with Derek Parker, a renowned veteran with six decades of experience in healthcare design, the pair could be set to revolutionize the way that hospitals are designed and built.
In June 2011, Derek Parker boarded a plane at San Francisco International Airport. The veteran health-care architect was headed to San Diego to deliver the most improbable presentation of his illustrious, six-decade-long career. For six months, he had worked as a consultant with a Silicon Valley design start-up called Aditazz. Shortly after Parker signed on, the new company had entered Small Hospital, Big Idea—a design competition launched by Kaiser Permanente. The first round, in which the firms remained anonymous, drew more than 400 entries. Eight of the nine shortlisted firms invited to San Diego were industry heavyweights. The ninth, to everyone’s surprise, was the unknown Aditazz.
Unified Architectural Theory: Chapter 2A

We will be publishing Nikos Salingaros’ book, Unified Architectural Theory, in a series of installments, making it digitally, freely available for students and architects around the world. The following chapter, part one of Chapter Two, outlines the scientific approach to architectural theory. If you missed them, make sure to read the introduction and Chapter One first.
In order to discuss any supposed contributions to architectural theory, it is necessary to define what architectural theory is. A theory in any discipline is a general framework that:
(1) explains observed phenomena;
(2) predicts effects that appear under specific circumstances; and
(3) enables one to create new situations that perform in a way predicted by the theory.
In architecture, a theoretical framework ought to explain why buildings affect human beings in certain ways, and why some buildings are more successful than others, both in practical as well as in psychological and aesthetic terms.
Keep Talking Kanye: An Architect's Defense of Kanye West

I may be in the minority among my peers, but I want Kanye West to keep talking. Despite the many who despise, disparage or dismiss him—unwilling or unable to properly digest what he’s saying, consuming bite-sized quotes and late-night parodies instead of engaging him in intellectual discourse—I want him to keep talking.
As a black man and an architect (one of about 2,000 in this country who can claim membership to both those groups), I am particularly cognizant of the Truman Show wall that exists between architects and recognition, and between black architects and acceptance. West's recent interview with Zane Lowe administered reflections on design, architecture and the creative process in a dosage too high for most to swallow. I am tripping over myself with fear and excitement at the prospect of having such a powerful mouthpiece for a generation of black architects and designers who share his frustration and connect with his message.
Why? Because when Kanye West talks, people listen.
An Interview with Magda Mostafa: Pioneer in Autism Design

In 2002, Magda Mostafa, a then-PhD student at Cairo University, was given an exciting project: to design Egypt's first educational centre for autism. The young architect set herself down to the task of researching into autism design, certain she'd soon find guidelines and accessibility codes to direct her through the process (after all, about one in every 88 children is estimated to fall into the autism spectrum).
But, as Mostafa told me, "I had a rude awakening; there was virtually nothing."
So she started setting up studies to gather the evidence she'd need to come up with her own guidelines. And she was breaking ground: a study she completed in 2008 was "among the first autism design studies to be prospective not retrospective, have a control group, and measure quantifiable factors in a systematic way."
Since those uncertain beginnings, Mostafa has positioned herself as one of the world's pre-eminent researchers in autism design. Her latest work, summarized in "An Architecture for Autism," the journal IJAR's most downloaded article in 2012, outlines Mostafa's latest accomplishment: the Autism ASPECTSS™ Design Index, both a matrix to help guide design as well as an assessment tool "to score the autism-appropriateness of a built environment" post-occupancy. In the following interview, we discuss the Index, the potential of evidence-based design for architecture, and what it's like to break ground (and try get funding) in a country where "black-outs, security threats, water shortages and unbelievable traffic" are everyday occurrences.











