In the Negev Desert of Israel, SAGA Space Architects are collaborating with D-MARS to build a Mars Lab Habitat that will simulate the conditions of living in a confined space on the hazardous surface of the red planet. The laboratory structure they’ve designed is an addition to D-MARS' existing Mars simulation habitat and will be part of a larger experiment. This habitat will serve as a prototype for a longer mission scheduled for 2020.
Mars: The Latest Architecture and News
SAGA Space Architects Design Simulated Mars Habitat in Israeli Desert
SEArch+ and Apis Cor Win Latest NASA Competition for 3D Printed Habitats on Mars
.jpg?1554130599&format=webp&width=640&height=580)
SEArch+ and Apis Cor have won first place in the Virtual Construction level of NASA’s 3D-Printed Habitat Centennial Challenge, seeking to create sustainable shelters suitable for the Moon, Mars, and beyond. Using resources available on-site in these locations, the female-led, New York-based space research and design practice proposed the MARS X HOUSE, offering a robust, durable 3D-printed habitat using autonomous robotics.
Led by SEArch+ co-founder Melodie Yashar, the scheme employs evidence-based design for the form and constructability of the future habitat, intended for a crew of four to live and work on Mars for one Earth year. The habitat is designed to exceed radiation standards in order to ensure human health while connecting the crew with natural light and views of the Martian landscape.
AI SpaceFactory Builds 3D Printed Mars Prototype for NASA

Architecture and technology company AI SpaceFactory has completed the autonomous construction of MARSHA, a proposal for a Martian surface habitat for NASA. The 3D printed shelter is one of five finalists in an international competition to design and build a habitat for a crew of four astronauts on a mission to Mars. AI SpaceFactory formulated their own material – a “Martian polymer” that can be made from matter found or grown on the planet.
This Week in Architecture: Visions from the Future
NASA Endorses AI SpaceFactory's Vision for 3D Printed Huts on Mars

AI SpaceFactory has released details of their proposed cylindrical huts for the Planet Mars, designed as part of the 3D Printed Habitat Challenge organized by NASA. Project MARSHA (Mars HAbitat) was endorsed by NASA with a top prize of almost $21,000, one of five designs selected from a field of seventeen.
The competition asked participants to design an effective habitat for a crew of four astronauts to be located on the Red Planet, using construction techniques enabled by 3D printing. The submitted schemes were then ranked based on their innovation, architectural layout, and level of detail in BIM modeling.
Life on Mars? Foster + Partners to Showcase Extra-Terrestrial Habitats at UK's Goodwood Festival
.jpg?1530807729&format=webp&width=640&height=580)
Foster + Partners will detail its vision of life on Mars and the Moon at the UK’s Goodwood Festival of Speed 2018. Forming part of the festival's Future Lab event, the vision will be presented through a range of models, robotics, and futuristic designs exploring the future of life in space.
The firm's showcase will include a virtual reality experience, allowing visitors to explore the inside of a proposed state-of-the-art habitation pod.
Elon Musk Announces SpaceX Plans to Begin Mars Colonization by 2022
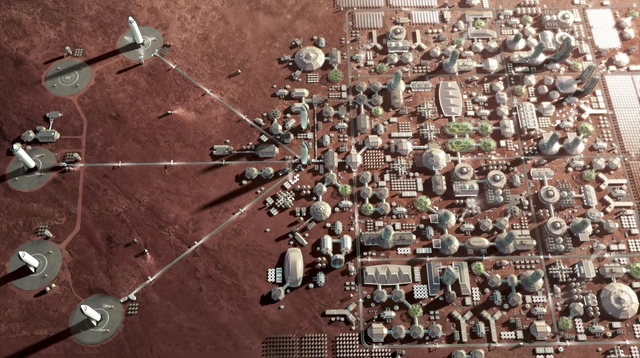
At this morning’s International Astronautical Congress in Adelaide, Australia, SpaceX founder and Lead Designer Elon Musk announced the most ambitious plans yet for the colonization of planets and satellites beyond Earth, including the establishment of a lunar base and a permanent Mars colony by 2022.
“The future is vastly more exciting and interesting if we’re a space-faring species than if we’re not,” said Musk during his keynote. “It’s about believing in the future and thinking the future will be better than the past.”
UAE Announces $140 Million BIG-Designed Mars Science City

The government of the United Arab Emirates has announced the launch of the Mars Science City project, a $140 Million USD (AED 500 million) research city that will serve as a “viable and realistic model” for the simulation of human occupation of the martian landscape. Designed by a team of Emirati scientists, engineers and designers from the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre in partnership with Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG), the 1.9 million-square-foot domed structure will become the largest space simulation city ever constructed.
Foster + Partners and Branch Technology Win Phase 2 of NASA's 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge

The team of Foster + Partners and Branch Technology have been awarded first prize in the latest stage of NASA’s 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge, a $2.5 million multi-phase competition designed to generate ideas and advance technology for the construction of sustainable housing solutions “for Earth and beyond.”
After printing three cylinder and three beams the first two levels of Phase 2, Stage 3 asked teams to design and print a 1.5-meter dome using indigenous Martian soil and recyclable materials, envisioning how future habitats could be constructed on the Red Planet. Teams were required to develop the 3-D printing technology itself as well as the structural design for each dome. The competition also dictated each structure be built within a 22-hour time frame, using the specific materials, geometric tolerances and autonomous performance that would be demanded by the Martian landscape.
Foster + Partners Awarded Top Prize in NASA’s 3D-Printed Mars Habitat Challenge

NASA has announced the completion of the initial printing stage of NASA’s 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge, awarding Foster + Partners | Branch Technology and the University of Alaska, Fairbanks as the two top-scoring teams from this round.
After Phase 1 of the competition (won by Clouds AO and SEArch) tasked architects and engineers from around the globe to imagine hypothetical concepts for the habitation of Mars, Phase 2 is challenging designers to manufacture actual, 3D-printed objects using techniques that could be employed to create shelters on a future mission to the red planet or beyond.
KieranTimberlake is Using Virtual Reality to Design a Home for Future Life on Mars

This article was originally published by Autodesk's Redshift publication as "Life on Mars? Architects Lead the Way to Designing for Mars With Virtual Reality."
If an architecture firm is lucky, it can hit two birds with one stone on a single project—for example, prioritizing both historic preservation and energy efficiency. But a team at KieranTimberlake, based in Philadelphia, is aiming for four ambitious goals with its pro bono project, the Mars City Facility Ops Challenge.
Architects Fátima Olivieri, Efrie Friedlander, and Rolando Lopez teamed up with National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS), NASA, and the Total Learning Research Institute (TLRI) to create a virtual working city on Mars—one that might reap multiple rewards.
This Mars Colonization Proposal Would 3D Print Biodegradable Fungus Towers that Leave No Trace

After NASA’s discovery of water beneath the surface of Mars earlier this year, and the subsequent critical and popular success of the movie The Martian, it's safe to say that the planet named after the God of War is all the rage. Those revelations have led to speculative looks at how our neighboring planet could be colonized from numerous designers, such as Norman Foster.
Many of those plans, including those of SpaceX founder Elon Musk, involve dumping Earthen construction materials onto the alien surface, potentially starting an inclination for pollution of our new world before it is even occupied. Spanish architect Alberto Villanueva of IDEA Architecture Office saw this as an opportunity for design to intervene. Using Martian soil and the fungus mycelium, Villanueva proposes a strategy utilizing 3D printing and bioluminescence that has gained the attention of both NASA and the European Space Agency.
Will This Be the Concrete Used to Build on Mars?

"All we need now are a new generation of Martian architects to design buildings made of Martian concrete that will be suitable structures for humans to live and work in," concludes the MIT Technology Review in their report on a new type of concrete designed for use on Mars.
Developed by scientists led by Lin Wan at Northwestern University, this "Martian concrete" is just one of many scientific developments that will be required for the increasingly popular goal of sending humans to, and eventually colonizing, the Red Planet (apparently the un-colonized Moon is already old hat - just ask Matt Damon).
Clouds AO and SEArch Win NASA's Mars Habitat Competition with 3D-Printed Ice House
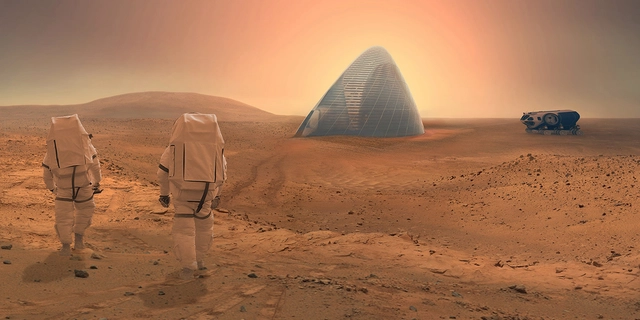
NASA, who recently confirmed evidence of flowing water on Mars, has deemed SEArch (Space Exploration Architecture) and Clouds AO (Clouds Architecture Office) winners of the 3D Printed Habitat Challenge for Mars. Sponsored by NASA and America Makes, the teams were asked to use indigenous materials and 3D printing techniques to build a habitat for four astronauts on Mars. SEArch and Clouds AO's first prize proposal, ICE HOUSE was awarded $25,000, ahead of 30 other shortlisted practices.
"Recognizing that water is the building block to life, the team used a ‘follow the water’ approach to conceptualize, site and construct their design," said SEArch and Clouds AO. "[Our] proposal stood out as one of the few entries not to bury the habitat beneath regolith, instead mining the anticipated abundance of subsurface ice in the northern regions to create a thin vertical ice shell capable of protecting the interior habitat from radiation while celebrating life above ground."
Foster Among 30 Shortlisted in NASA-Backed Mars Habitat Competition

Foster + Partners has been shortlisted among 30 other finalists in the 3D Printed Habitat Challenge organized by America Makes and NASA. The proposal calls for a 3D printed settlement built by pre-programmed, semi-autonomous robots who use regolith found on Mars' surface to construct dwellings that can house up to four astronauts each.
"The proposal considers multiple aspects of the project from delivery and deployment to construction and operations," says Foster. "The habitat will be delivered in two stages prior to the arrival of the astronauts."











.jpg?1554130599)
























