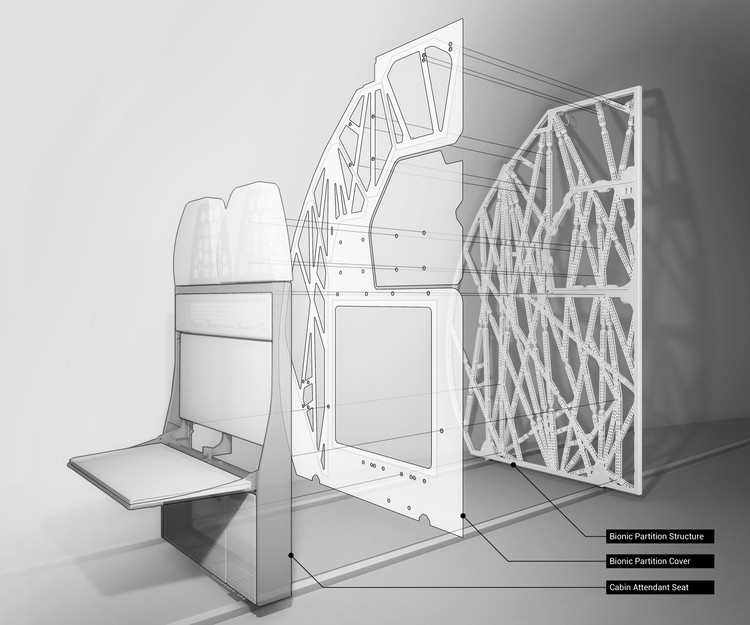
You’ve probably never given much thought to the seemingly basic interior partitions of an airplane, but building codes are a walk in the park compared to the exacting standards of aviation design. Those thin panels that separate the seats from the plane's galley must also be capable of supporting the weight of flight attendant jumpseats and providing a removable section to accommodate emergency stretchers - not to mention the rigorous safety standards and crash testing that aviation components must satisfy. With all of these challenges in mind, The Living, an Autodesk Studio, in collaboration with Airbus and APWorks, have developed the Bionic Partition Project, which harnesses generative design and 3D printing to maximize the structural efficiency of the panel, reducing the weight of an aircraft, and saving fuel. And while this particular application is specific to a single aircraft type, the technological advances could have far-reaching implications.